What Is Project Management And Why Do You Need It
Project management methods are the ways that project managers plan, execute, and monitor their projects. Different methods have different advantages and disadvantages depending on the type, scope, and complexity of the project. Not all project management methods work for all types of projects. So it is important to keep in mind which method you can best use for a given project or phase of a project.
Here are some of the common project management methods that researchers and academics can use and their characteristics:
The Waterfall Method
Waterfall is a project management methodology that follows a sequential and linear process, where each phase of the project is completed before moving on to the next one.
Originally developed for use in computer science waterfall has since been adopted in other fields as well. It is suitable for projects that have clear and fixed requirements, and that do not require much feedback or iteration.
Some use cases for academics who might adopt the waterfall project management methodology are:
- Writing the first draft of a dissertation or a thesis, where the research question, literature review, methodology, data collection, analysis, and conclusion are done and submitted in a logical and orderly manner (at least in theory).
- Conducting a laboratory experiment, where the hypothesis, design, procedure, results, and discussion are clearly defined and followed.
- Developing a curriculum or a course, where the learning objectives, content, activities, assessments, and evaluations are planned and executed in a structured way.

Pros
Cons
- It provides a clear and detailed plan for the project, which helps to define the scope, schedule, budget, and quality.
- It facilitates communication and documentation, as each phase has specific deliverables and expectations.
- It reduces the risk of errors and changes, as each phase is tested and verified before moving to the next one
- It lacks flexibility and adaptability, as it does not allow for changes or revisions once a phase is completed.
- It reduces stakeholder involvement, as it does not incorporate feedback or collaboration during the project.
- It delays the delivery and value of the project, as it does not produce a working product or feature until the end of the project.
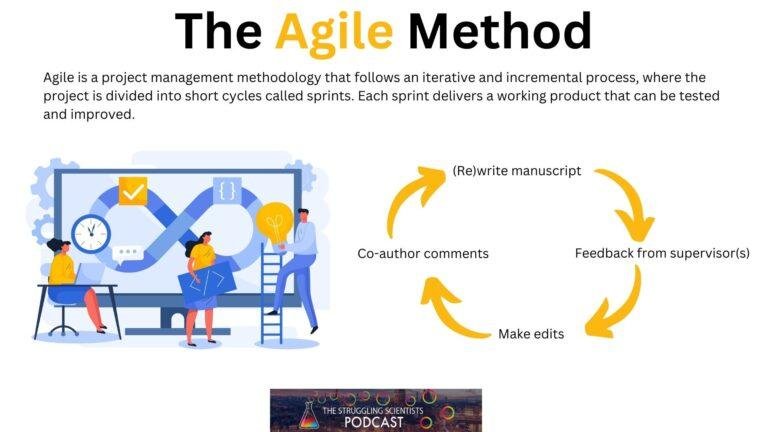
The Agile Method
Agile is a project management methodology that follows an iterative and incremental process, where the project is divided into short cycles called sprints. Each sprint delivers a working product or feature that can be tested and improved. It is suitable for projects that have changing or uncertain requirements and deliverables, and that allow for more collaboration and feedback.
Here are some use cases for academics who might adopt the agile project management method:
- Developing a software or a tool, where the functionality, design, and usability can be refined and enhanced based on user feedback and testing.
- Conducting fieldwork or a survey, where the research question, design, and methodology can be adjusted and modified based on the data collected and the context encountered.
- Writing a paper or a grant proposal, where the structure, content, and style can be improved and polished based on peer review and feedback. Or rewriting the paper to submit it to another journal once it’s rejected.
Pros
Cons
- It provides flexibility and adaptability, as it allows for changes and revisions during the project.
- It incorporates feedback and collaboration throughout the project.
- It delivers value and impact early and frequently, as it produces something in each sprint.
- It can be difficult to estimate the time and cost of the project, as it depends on the scope and complexity of each sprint.
- It requires a high level of commitment and communication from the team, as it involves frequent meetings and interactions.
- It can be challenging to integrate and coordinate different sprints, as it may result in inconsistency and duplication.
The Kanban Method
Kanban is a workflow management method that allows project managers to visualize their team’s work on easy-to-use boards that facilitate the process of planning, scheduling, and tracking work. It is suitable for projects that require flexibility and adaptability, and that have a high volume of repetitive tasks.
Some use cases for academics who might adopt the Kanban project management are:
- Managing a research project, where the team can use the Kanban board to track the progress of the literature review, data collection, analysis, and writing.
- Organizing a conference or a workshop, where the team can use the Kanban board to manage the logistics, the schedule, the speakers, and the attendees.
- Developing a course or a curriculum, where the team can use the Kanban board to design the learning objectives, the content, the activities, and the assessments.

Pros
Cons
- It provides flexibility and adaptability, as it allows the team to adjust and prioritize the tasks based on the changing needs and requirements of the project.
- Kanban enhances transparency and collaboration, as it enables the team to share and communicate the progress and status of the tasks with eachother.
- It also improves efficiency and quality, as it reduces the time and effort spent on planning, discussing, and resolving issues, and thus ensures that the tasks are completed in a timely and consistent manner.
- It can be challenging to manage and maintain, as it requires a clear and consistent process and quality for the tasks, and it may result in confusion and inconsistency if not followed properly.
- It can be difficult to scale and integrate, as it may involve multiple boards and teams that need to be aligned and coordinated.
- It can reduce creativity and innovation, as it may focus on the execution and optimization of the tasks rather than the exploration and experimentation of new ideas and methods.
The Scrum Method
Scrum is a specific type of agile project management that emphasizes teamwork, communication, and continuous improvement. It is suitable for academics who work on research projects that require cross-functional collaboration, creativity, and innovation. Scrum allows academics to work in self-organizing and cross-functional teams called scrum teams that are responsible for delivering a working product or feature in each sprint. This approach enables academics to foster a culture of trust, transparency, and accountability among their team members.
Some use cases of Scrum project management for academics are:
- The early stages of conducting a research project that requires frequent feedback and iteration, such as a literature review, a survey, or a case study.
- Developing software or a tool that requires cross-functional collaboration, such as a data analysis tool, a simulation model, or a visualization platform.
- Writing a book or a journal article that requires a structured and collaborative approach, such as a co-authoring project, a peer review process, or a writing workshop.

Pros
Cons
- It enhances teamwork and communication, as it involves frequent and transparent interactions among the team members.
- It fosters creativity and innovation, as it encourages experimentation and feedback in the development process.
- It improves quality and satisfaction, as it delivers value and impact in each sprint and responds to the changing results.
- It requires a high level of trust and commitment, as it relies on the self-organization and empowerment of the team.
- Scrum can be difficult to scale and coordinate, as it may involve multiple scrum teams that need to be integrated and aligned.
- It can be challenging to manage and document, as it may not follow a formal and standardized process or produce a comprehensive and detailed plan.
The Lean Method
Lean is a project management style that emphasizes value, flow, and pull. It is suitable for academics who work on research projects that require efficiency, productivity, and quality. Lean allows academics to identify and eliminate non-value-added activities, reduce time, and improve satisfaction. This approach enables academics to optimize their research process by focusing on the most important aspects, and the flow of work.
Some use cases of Lean project management for academics are:
- Conducting a literature review or a meta-analysis, where you can use Lean principles to identify and eliminate redundant or irrelevant sources, reduce the time and effort spent on data extraction and analysis, and improve the quality and relevance of the findings.
- Developing a research proposal or a grant application.
- Writing a journal article, where you identify and eliminate non-value-added activities, such as excessive editing or formatting, reduce the feedback time with co-authors, and improve the readability and relevance of the content for the journal.

Pros
Cons
- It provides efficiency and clarity, as it reduces the time and effort spent on planning, discussing, and resolving issues.
- Lean ensures consistency and quality, as it follows a standardized and rigorous process and produces a clear and detailed plan.
- It enhances accountability and responsibility, as it assigns specific roles and tasks to the team members and monitors their performance.
- It limits the input and involvement of the team, as it does not incorporate feedback or collaboration during the project.
- It creates a negative and stressful work environment, as it may cause resentment, frustration, and dissatisfaction among the team members and the stakeholders.
- It reduces creativity and innovation, as it does not encourage experimentation or feedback in the project development and improvement.
Final Thoughts
Knowing which project management method to use and when can save you a lot of headaches and trouble down the road. While there may be some overlap between the different project management methods they also possess unique characteristics that make them specifically well-suited to certain projects or parts of a project over others so keep those in mind when selecting which method to use.
If you found this useful consider checking out our other blogs on how to overcome procrastination or how to take efficient notes which are extremely useful skills to develop for all struggling scientists out there.
Rather watch a YouTube video or listen to a podcast on Spotify instead?
For more success on your academic journey consider watching our episode on the Tenure track with Emmanuel Tsekleves either on Youtube or Spotify. Or if you’re considering leaving academia then check out our episode with Ashley Ruba on Youtube or Spotify instead.